Benchmark Construction
We assigned three annotators (selected from the authors) to each of the four simulated websites. To ensure consistency in task quality across different websites, one annotator was assigned to all four websites. In total, ten annotators were involved in the task creation process. This annotation process was both meticulous and labor-intensive, totaling over 300 hours.
1. Emphasis on Memory-intensive Analytical Tasks.
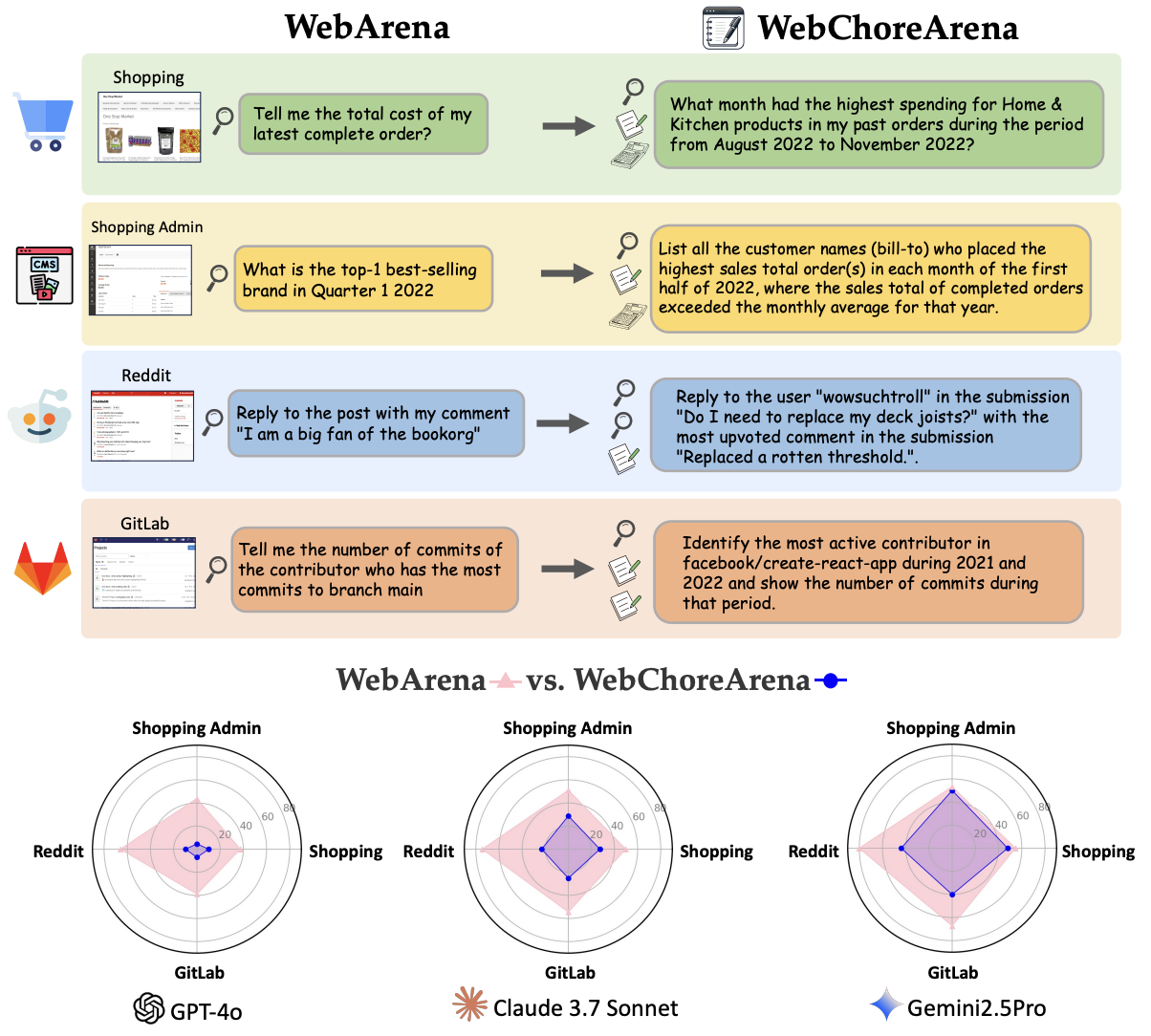
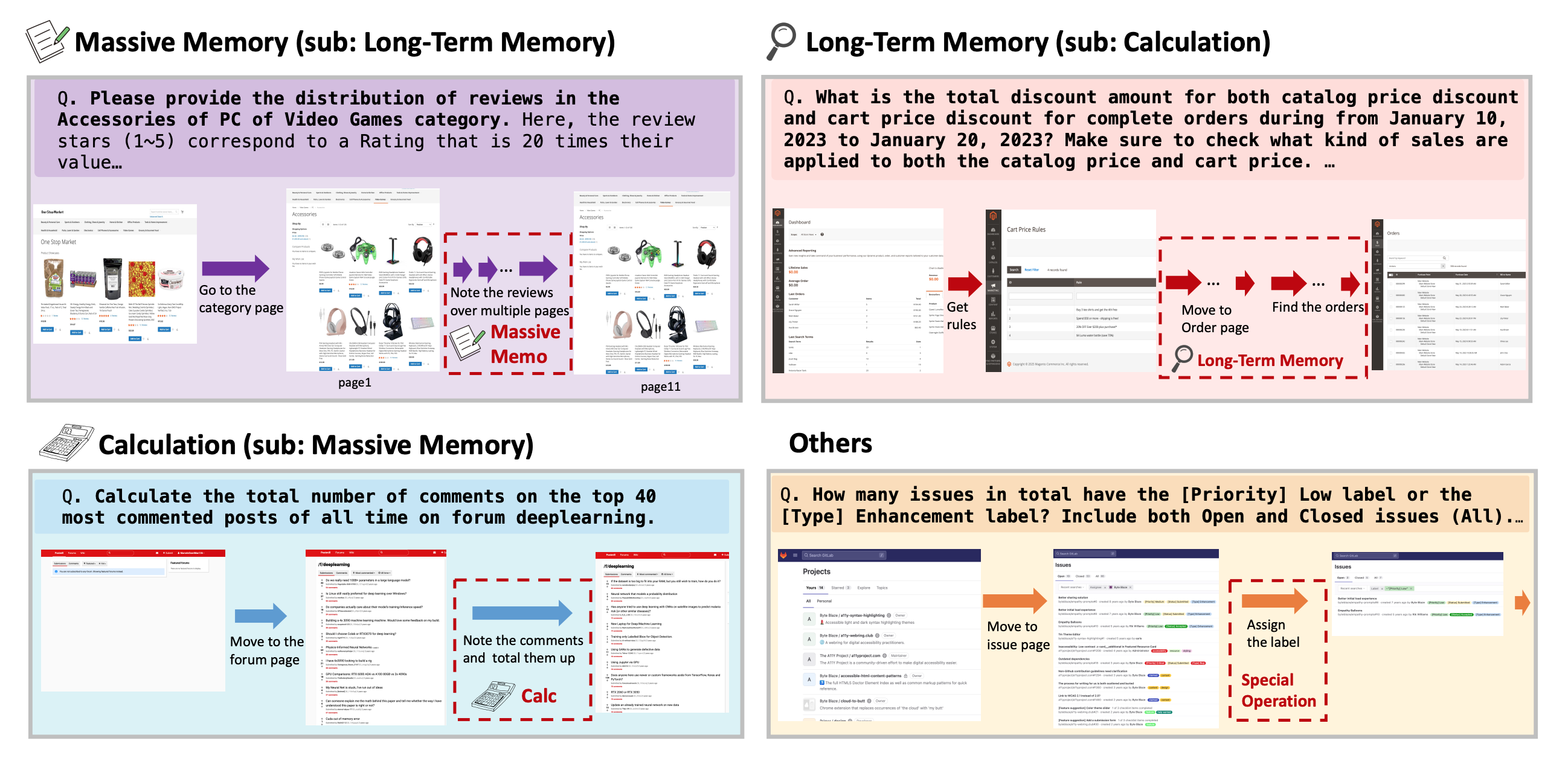
We deliberately focused on collecting tasks that require memory—that is, tasks in which information from past observations is essential to reach the correct answer. Such tasks are common in real-world scenarios but remain largely underrepresented in existing benchmarks such as WebArena.
To avoid overly simplistic tasks, we first prototyped early task ideas and evaluated them using a Claude-based agent to identify model limitations and refine the task designs. This process ensured that our final tasks were both meaningful and appropriately challenging.
2. Reducing Ambiguity in Task Specification and Evaluation.
We explicitly instructed annotators to eliminate ambiguity in both task descriptions and evaluation criteria. While handling ambiguous instructions is important for agents aiming to operate flexibly in real-world human interactions, we prioritized clear evaluability, since reliable evaluation is essential for measuring progress.
In WebArena, vague instructions often lead to scenarios where agents produce reasonable answers that are incorrectly marked as failures. In addition, we observed that the evaluation protocol in WebArena can fail to reliably assess answers due to vague output format expectations. To mitigate ambiguity in answer evaluation, we standardized the required output formats, e.g., "Provide only the answer without any additional words.", when aiming for exact matching with the ground truth.
3. Template-based Task Construction and Extension.
Following WebArena, we instructed annotators to create task templates and extend them to several task instances. The annotators were also responsible for developing several instantiations for each variable. This templated design enables a more robust and systematic evaluation of agent performance across tasks that share semantic similarity but exhibit diverse execution traces.
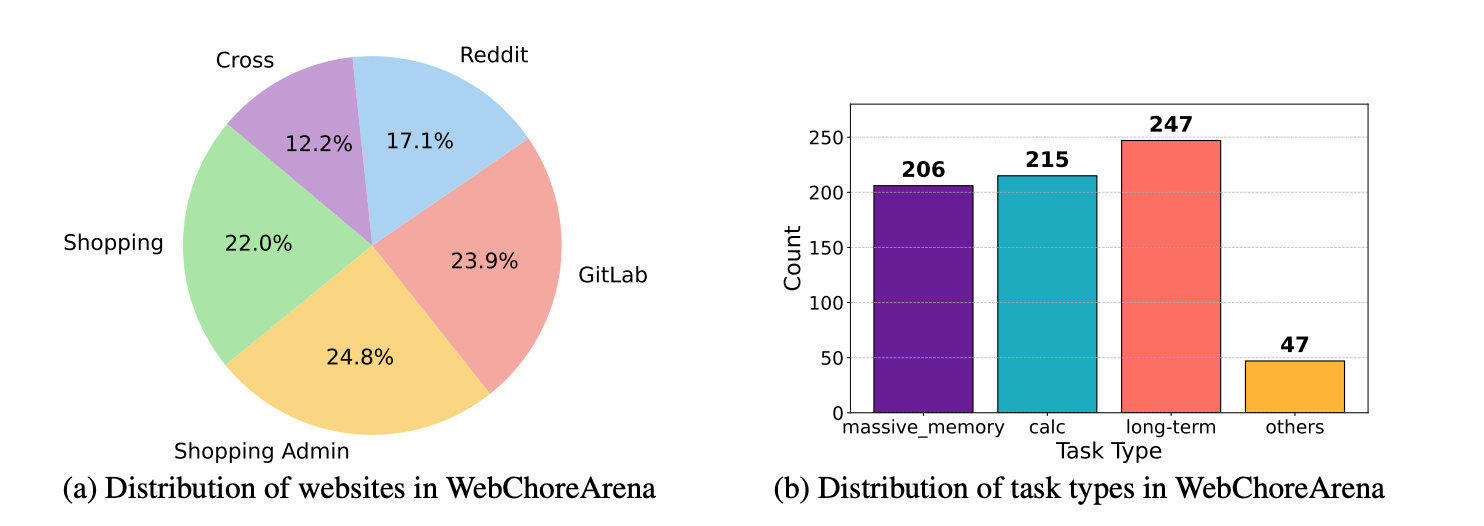
We created a total of 117 task templates: 25 for Shopping, 29 for Shopping Admin, 20 for Reddit, 28 for GitLab, and 15 for Cross-site tasks. On average, each template yielded approximately 4.5 task instances. Here, WebArena includes several tasks based on the map website (OpenStreetMap).